Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
SEPTA Regional Rail R5: Paoli/Thorndale – Lansdale/Doylestown Line
$30.00 – $80.00
Additional information
| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 3 × 3 × 24 in |
| Size | Framed 18"x24", 18" x 24", 24" x 36 |
Related products
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The Bay Area Rapid Transit system (BART) was, along with the WMATA in Washington D.C., one of the great centrally planned post-war rapid transit systems aimed at addressing the rise of the highway and auto-centric suburbs after World War II in the United States. Planning began in the 1950s for a unified high speed rail system that would serve both the dense inner cities of San Francisco and Oakland and their newly expanding low-rise suburbs. Stations would be spaced closer in the central business districts and further out in the suburbs.
Originally planned to connect Alameda, Contra Costa, Marin, San Francisco, and San Mateo counties BART was scaled back when San Mateo dropped out in favor of commuter rail service and the Marin line was dropped due to engineering concerns about running a rail line over the Golden Gate Bridge. Construction began in 1964 and the initial segments began to come online in 1972 and the majority of the system opening by 1974.
The Richmond-Warm Springs Line, also known as the East Bay Line, is the only line that does not enter San Francisco running from Richmond in the north through Oakland to Fremont in the south. Like most BART lines the Richmond-Fremont Line shares its tracks with other BART lines: the Richmond-Millbrae Line, the Pittsburg/Bay Point–SFO/Millbrae Line, the Fremont–Daly City Line, and the Dublin/Pleasanton–Daly City Line.
The Richmond–Fremont Line was the first of BART’s five lines to open. Service from MacArthur to Fremont began on September 11, 1972, the first day of BART operation and was extended to Richmond on January 29, 1973.
Construction has begun on a southern extension to San Jose; the first phase to Warm Springs/South Fremont opened in 2017 with the second phase to Milpitas and Berryessa opening in 2020.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00What today is the Blue Line started in 1895 as the Metropolitan West Side Elevated Railroad with service from Canal St to Logan Sq. Soon branches were added to Garfield Park, Humboldt Park, and Douglas Park. The Met, as it was known, has seen the most dramatic changes of all the Chicago “L” lines: the Humboldt Park and Logan Sq branches were removed when service was rerouted through the new Milwaukee-Dearborn Subway in 1951 and subsequently extended along the Kennedy Expressway to Jefferson Park in 1970 and then to O’Hare Airport in 1984. The Garfield Park branch was completely rebuilt along the median of Interstate 290 in 1958. In 2008 the Douglas Branch was rerouted along the Paulina Connector (a left over section of track from the old Logan Sq branch) to connect to the Loop and rebranded as the Pink Line.
The modern sections of the Blue Line were the first examples of rapid transit running along a high median in the US. The Blue Line, along with the Red Line, are the only two services of the CTA which run 24 hours a day.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 $30.00 – $80.00
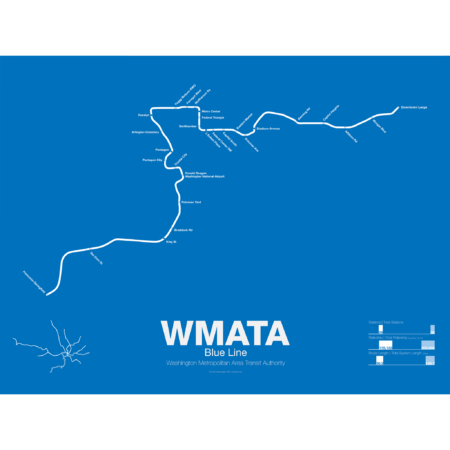
$30.00 – $80.00The Blue Line was the second section of the Washington Metro to open; on July 1st 1977 trains began running the familiar serpentine route from National Airport through Roslyn and Metro Center (at the time the only transfer station) to Stadium-Armory. In 1978 an extension to New Carrollton opened and service was split between Blue Line trains running from National Airport-New Carrollton and Orange Line trains running the reverse direction. When the Orange Line extension to Ballston opened a year later Blue Line trains were cut back to Stadium-Armory.
When the Addison Road branch opened in 1980 the Blue Line once again ran only one direction while Orange Line trains ran in the other direction, this time on both branches. In 1983 the Yellow Line was opened down to Huntington. This was originally to be the new terminal for Blue Line trains but due to a car shortage the Yellow Line, which required fewer cars, was extended instead, and this service pattern remains to this day. The extension to Van Dorn St (the originally planned terminal for the Yellow Line) didn’t open until 1991 and was extended to Franconia-Springfield in 1997. A final extension to Largo Town Center opened in 2004.
The Blue Line holds the distinction of the line which shares the most amount of track with other lines (the Orange and Yellow lines). In fact during rush hour service only the Arlington Cemetery station is served exclusively by Blue Line trains. Because of this, planners are looking at digging a new tunnel through central D.C. once the Silver Line opens which is also slated to share Blue Line tracks through downtown D.C.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 $30.00 – $80.00
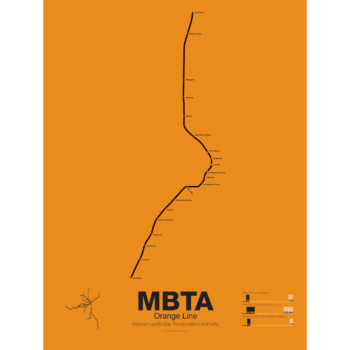
$30.00 – $80.00First opened in 1901 the Orange Line was the second part of Boston’s subway system to open. The tunnel under Tremont St was converted from trolleys to heavy rail to allow the new elevated trains from Charlestown to run through to Dudley Sq. in the South End. A second elevated section known as the Atlantic Ave El ran from Castle Sq. in the South End to North Station along Atlantic Ave to serve the maritime industries along the waterfront. In 1904 the Washington St tunnel was opened specifically for use by elevated trains and the Tremont St subway was switched back for trolley use.
The Orange Line was designed to collect commuters at elaborate transfer stations in Charlestown and Roxbury and quickly move them downtown. Suburban stations were spaced farther apart and downtown station platforms were built catty-corner from one another. This spread commuters out so that Boston’s notoriously narrow streets would not be over crowded by subway passengers.
As the city grew so did the Orange Line being extended to Forest Hills and Everett (a further extension to Malden was halted until the 1970s). As the maritime industry faded and ridership dropped the Atlantic Ave El was demolished and sold for scrap during World War II.
While the El served the city well it was not popular as it was loud, dark, and dirty. Plans were laid as early as 1945 to remove the El and rebuild as a subway.
In the 1970s the city canceled ambitious plans to run highways through and around the city and monies were transferred to subway construction. The northern section was rebuilt first, removing the elevated tracks through Charlestown and moving them west along a new subway to Malden in 1975.
The southern section was rebuilt along the route for the canceled I-95 expressway through Jamaica Plain to Forest Hills in 1987. While the new Orange Line was modern and fast the new route bypassed the existing community of Roxbury which relied heavily on mass transit. Service along the old route was replaced by the Silver Line bus in 2002.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page



