T
7 Products
- Please choose product options by visiting Boston MBTA Track Map v3: Complete and Geographically Accurate.
-
 $30.00 – $80.00
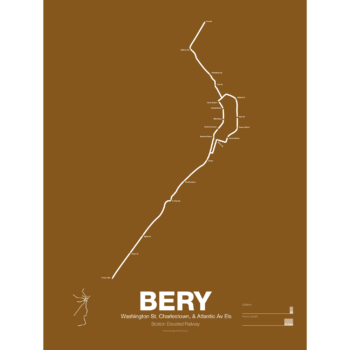
$30.00 – $80.00What is today the Orange Line was part of the original Boston Elevated Railway subway and elevated network. Today the only section remaining is the Washington St Tunnel from Haymarket to Chinatown. Originally there were two lines through downtown: the Main Line and the Atlantic Ave El. The Main Line served elevated branches from Charlestown and along Washington St to Dudley Sq. in the South End. The Atlantic Ave El ran from Castle Sq. in the South End to North Station along Atlantic Ave to serve the maritime industries along the waterfront.
As the city grew so did the elevated lines, being extended to Forest Hills and Everett (a further extension to Malden was halted until the 1970s). As the maritime industry faded and ridership dropped the Atlantic Ave El was demolished and sold for scrap during World War II.
While the El served the city well it was not popular as it was loud, dark, and dirty. Plans were laid as early as 1945 to remove the El and rebuild as a subway.
In the 1970s the city canceled ambitious plans to run highways through and around the city and monies were transferred to subway construction. The northern section was rebuilt first, removing the elevated tracks through Charlestown and moving them west along a new subway to Malden in 1975.
The southern section was rebuilt along the route for the canceled I-95 expressway through Jamaica Plain to Forest Hills in 1987. While the new Orange Line was modern and fast the new route bypassed the existing community of Roxbury which relied heavily on mass transit. Service along the old route was replaced by the Silver Line bus in 2002.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
-
 $375.00 – $500.00
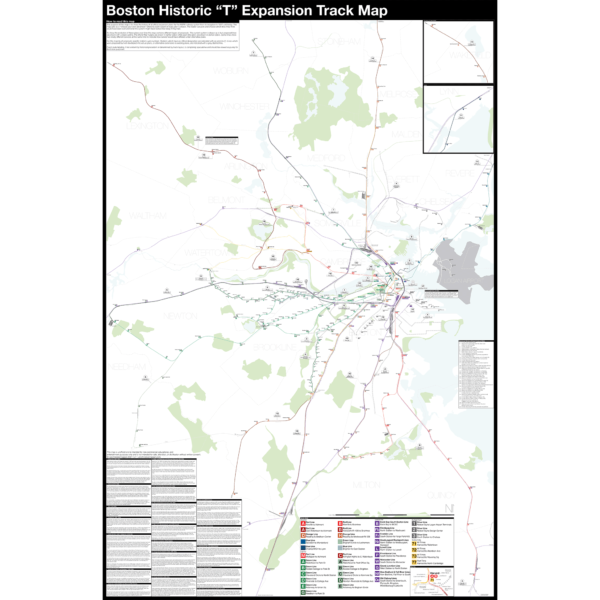
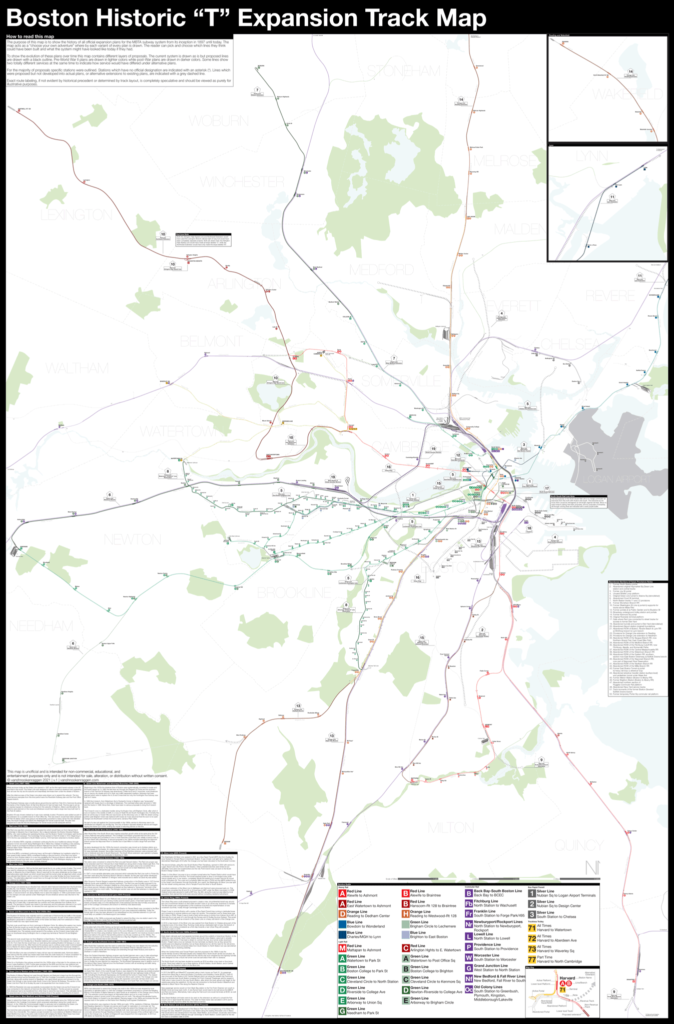
$375.00 – $500.00Boston opened the first subway in the US in 1897 and immediately began expanding it. Since then numerous plans have been drawn up, some are simple extensions while others are whole sale reimaginations of the subway. This map shows in detail each official proposal with the history of each idea.
The map acts as a “choose your own adventure” where by each variant of every plan is drawn. The reader can pick and choose which lines they think could have been built and what the system might have looked like today if they had.
Fine art prints are made in Williamsburg, Brooklyn NY on Semi-Gloss, 10mil Premium Luster Paper.
For more information about the map see the original blog post here.
-
 $325.00 – $450.00
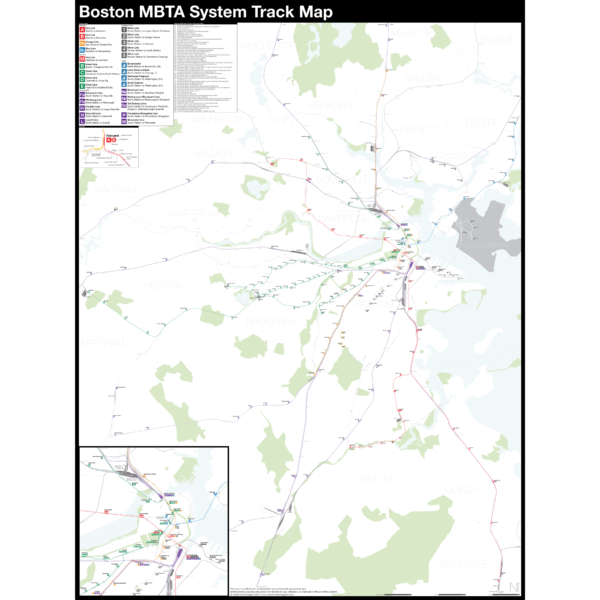
$325.00 – $450.00NEW version 3 with Green Line Extension!
The Complete and Geographically Accurate Boston MBTA Subway Track Map is a new detailed look at the subway system that most riders never see. Unlike a traditional subway map which just shows train routes, stations, and a simplified geography for easier navigation, the Track Map shows how the system actually looks; each track, each switch, each station platform and each train yard is shown in a clear and clean design. While the Track Map offers a service guide it is not intended to replace the subway map as a wayfinding tool. The Track Map shows the paths of the tracks so that the viewer can see how trains are able to run. If you’ve ever wondered why certain trains don’t run to certain places this map will tell you why.
The idea behind this was to remove all distortion from traditional subway maps and see the system down to its bones. Street labels, parks, cemeteries, and airports help act as landmarks. The more complicated interchanges and interlockings are shown in a blown up detail section along with a list of as many provisions and abandoned sections of the system I have discovered.
Fine art prints are made in Williamsburg, Brooklyn NY on Semi-Gloss, 10mil Premium Luster Paper.
For more information about the map see the original blog post here.
-
 $30.00 – $80.00
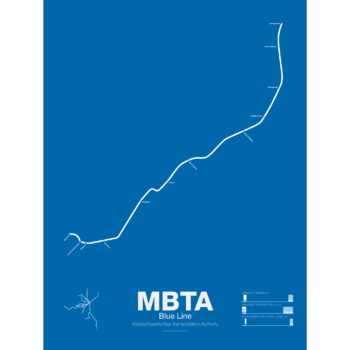
$30.00 – $80.00The Blue Line started off as a trolley tunnel to connect Scollay Sq. in downtown Boston to Maverick Sq. in East Boston. It holds the distinction as the first underwater transit tunnel (under a major body of water) opening in 1904. Initial plans called for it to be connected to the Green Line to form a subway trolley network connection all points north, east, south, and west. However, in 1924, the line was converted to heavy rail and extended to Bowdoin Sq. The Blue Line diverted traffic away from East Boston ferries which, ironically, helped bring the demise to the Atlantic Ave elevated line.
Until the 1950s the Blue Line was connected to the Red Line at Charles St so that Blue Line trains could be serviced at the Red Line train shops in Harvard Sq. In 1952 the Blue Line was extended to Suffolk Downs along the abandoned Boston, Revere Beach and Lynn Railroad and two years later extended to Revere where it still terminates at Wonderland.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The Green Line is part of the oldest subway in the United States. The short section between Boylston St and Park St opened in 1897 as a way to divert heavy trolley traffic which came downtown from Allston, Brighton, Brookline, Jamaica Plane, Roxbury, and Dorchester. It was quickly expanded to North Station to serve trolley traffic from the northern suburbs.
As commuting patterns changed due in part to the success of the subway the Green Line was extended west to Kenmore Sq and in the 1940s southwest along Huntington Ave. As more and more commuters chose to travel in private automobiles ridership on the trolleys dropped. In 1959 the Riverside branch was opened along a former commuter rail line through Newton. A rebranding of the MBTA system in 1967 renamed the branches that were left as the A, B, C, D, and E branches. The A branch to Watertown Sq. only lasted two more years before finally being axed in 1969.
Boston College B Branch trains run along Commonwealth Ave to Government Center; Cleveland Cirlce C Branch trains run along Beacon St to North Station; Riverside D Branch trains run along the Riverside line through Newton to Government Center; Heath St E Branch trains run along Huntington Ave to Lechemere. Construction has begun on a long planned extension northwest through Somerville which will bring the E branch to Union Sq and the D to College Ave-Tufts University.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
-
 $30.00 – $80.00
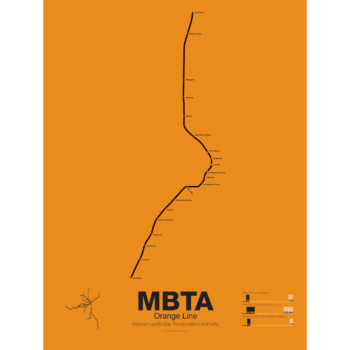
$30.00 – $80.00First opened in 1901 the Orange Line was the second part of Boston’s subway system to open. The tunnel under Tremont St was converted from trolleys to heavy rail to allow the new elevated trains from Charlestown to run through to Dudley Sq. in the South End. A second elevated section known as the Atlantic Ave El ran from Castle Sq. in the South End to North Station along Atlantic Ave to serve the maritime industries along the waterfront. In 1904 the Washington St tunnel was opened specifically for use by elevated trains and the Tremont St subway was switched back for trolley use.
The Orange Line was designed to collect commuters at elaborate transfer stations in Charlestown and Roxbury and quickly move them downtown. Suburban stations were spaced farther apart and downtown station platforms were built catty-corner from one another. This spread commuters out so that Boston’s notoriously narrow streets would not be over crowded by subway passengers.
As the city grew so did the Orange Line being extended to Forest Hills and Everett (a further extension to Malden was halted until the 1970s). As the maritime industry faded and ridership dropped the Atlantic Ave El was demolished and sold for scrap during World War II.
While the El served the city well it was not popular as it was loud, dark, and dirty. Plans were laid as early as 1945 to remove the El and rebuild as a subway.
In the 1970s the city canceled ambitious plans to run highways through and around the city and monies were transferred to subway construction. The northern section was rebuilt first, removing the elevated tracks through Charlestown and moving them west along a new subway to Malden in 1975.
The southern section was rebuilt along the route for the canceled I-95 expressway through Jamaica Plain to Forest Hills in 1987. While the new Orange Line was modern and fast the new route bypassed the existing community of Roxbury which relied heavily on mass transit. Service along the old route was replaced by the Silver Line bus in 2002.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00In 1912 the Red Line benefited from being the last of the original subways in Boston to open. A decade of subway building allowed the Red Line to be designed with larger trains and platforms that were easier to navigate (unlike the disconnected Orange Line platforms). Planned as an elevated subway until the citizens of Cambridge objected, the original route connected Harvard Sq. with Park St. At Harvard Sq. a parallel subway was built for trolleys to transfer commuters from the northwestern suburbs and is still in use today.
The Red Line was quickly extended to South Boston and large transfer stations were built at Broadway and Andrew Sq. to collect trolley (and later bus) commuters coming from Dorchester.
In 1926 and 1927 the Red Line was extended to Ashmont in Dorchester along the route of and old commuter rail road. Though the subway was proposed to be extended further to Mattapan the residents of Milton and southern Dorchester opted for a high speed trolley route instead, pre-dating the concept of light rail.
Plans were drawn up to create a new branch of the Red Line to Braintree as early as 1945 but construction didn’t begin for another 20 years. First to Quincy in 1971 and finally to Braintree in 1980 the new branch was designed to bypass Dorchester for a quicker commute.
At the other end the Red Line was extended northwest from Harvard Sq. to Alewife in 1985. Originally planned to run out to Lexington along the abandoned Boston and Maine Railroad the line was cut back when residents of Arlington protested.
The Red Line runs two heavy rail routes, Alewife-Ashmont and Alewife-Braintree (which skips Savin Hill).
A light rail section runs from Ashmont to Mattapan using refurbished PPC trolleys from the 1940s.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please allow more time for shipping.
