poster
105 Products
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The 6th Ave Line was the second half of the original IND system in Manhattan. The subway was built to replace the old 6th Ave elevated trains and, unlike the 8th Ave Line, was opened in sections between 1936 and 1968. The original sections expanded on the recently opened 8th Ave Line along Houston St to East Broadway, then under 6th Ave from West 4th St to 53rd St. The main trunk subway along 6th Ave was originally built with only two local tracks because of the existing PATH running under 6th Ave. Express tracks were not built until 1967.
B trains run only weekdays from 145th St in Manhattan to Brighton Beach via the Manhattan Bridge and the Brighton Line. At peak times B trains are extended into the Bronx to Bedford Park Blvd. D trains run all times from Norwood-205th St in the Bronx to Coney Island via the Manhattan Bridge, 4th Ave subway, and West End line (elevated). At peak times D trains run express along the Concourse subway. Both B and D trains run express in Manhattan, though B trains make all local stops from 59th St-Columbus Circle to 145th St.
F trains run express along the Queens Blvd subway and enter Manhattan via the 63rd St subway built in the 1960s as a part of the 2nd Ave subway. In Manhattan and Brooklyn F trains run local at all times. In Brooklyn the F shares part of its route with the IND G Crosstown line to Church Ave. After Church Ave the subway becomes elevated to Coney Island.
M trains once ran along the BMT Jamaica line to downtown Manhattan but in 2010 were rerouted along 6th Ave to Forest Hills replacing the short lived V train (which ran from Forest Hills to 2nd Ave). Elevated in Brooklyn, the M train runs through a section of tunnel, built in the 1960s but rarely used, to connect the 6th Ave line to the Williamsburg Bridge. M trains run all local weekdays and as a shuttle from Myrtle Ave to Middle Village nights and weekends.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-
 $30.00 – $80.00
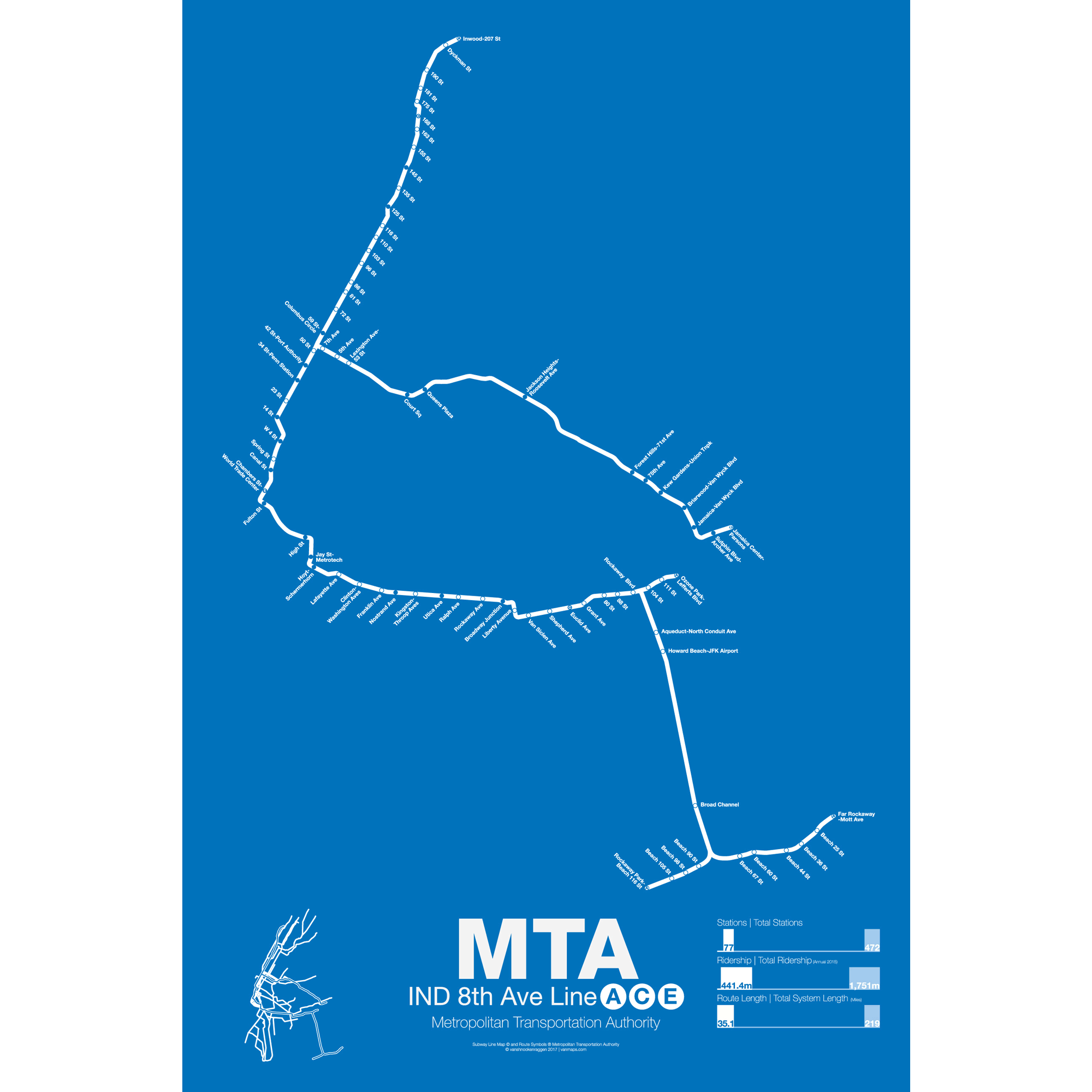
$30.00 – $80.00The 8th Ave Line was the first section to open as part of the Independent Subway (IND), a new system built and operated by the City of New York to compete with the privately run IRT in Manhattan and the Bronx and the BMT in Brooklyn and under Broadway. The first major section opened in September 1932 with express and local service from Washington Heights to Chambers St.
The 8th Ave Line shares its tracks with the 6th Ave trains along Central Park West and 53rd St. The A train (made famous by Billy Strayhorn’s Take the A Train) runs from 207th St in Inwood to Fulton St in downtown Manhattan as express while the C train runs all local from 168th St in Washington Heights to Fulton St. From there the line enters Brooklyn and runs out to Ozone Park along the Fulton St subway (not to be confused with Fulton St in Manhattan). The C train terminates at Euclid Ave while the A train continues on to one of three termini: Lefferts Blvd, Rockaway Park and Far Rockaway. The A is the only train with multiple, regular service, termini.
The E train runs local in Manhattan from World Trade Center to 50th St where it splits from 8th Ave under 53rd St heading east into Long Island City and Queens Plaza. The E train is one of the two workhorse express trains running along the Queens Blvd subway to Forest Hills and Jamaica. The E splits from the Queens Blvd subway at Van Wyck Ave and terminates in Jamaica Center.
The majority of the 8th Ave Line is underground and was built specifically for the IND system. The sections of elevated track after Euclid Ave to Lefferts Blvd were recaptured from the existing Fulton St elevated line in the 1940s and the tracks out to the Rockaways where added in the 1950s after being purchased from the Long Island Rail Road.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-
 $30.00 – $80.00
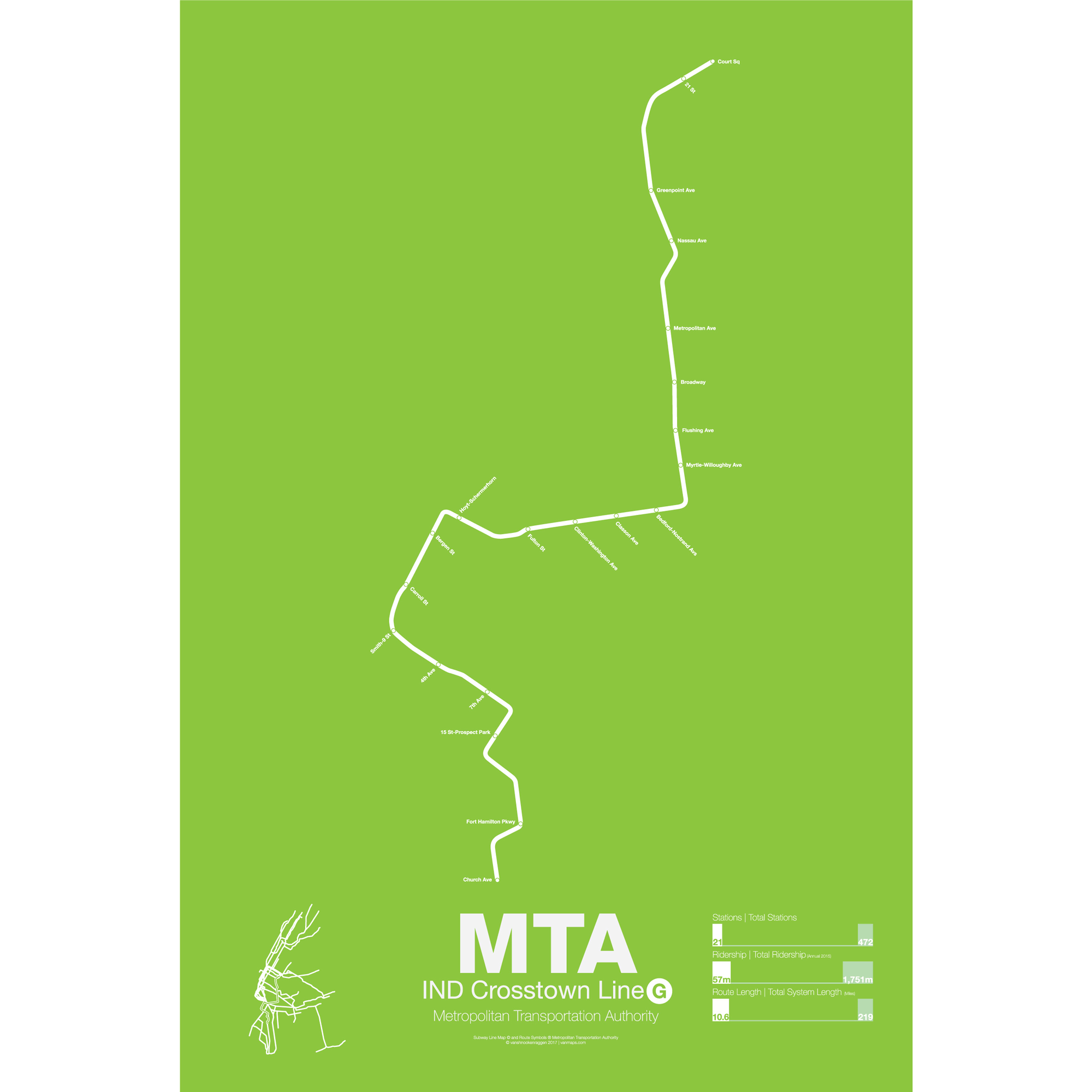
$30.00 – $80.00The IND Crosstown line holds the distinction of being the only subway line to never enter Manhattan. Running local between Court Sq in Long Island City, Queens and Church Ave in Kensington, Brooklyn, the G train was opened in segments from 1933 to 1937 to connect the IND Queens Blvd subway to the IND Fulton St and IND South Brooklyn subway. Original plans for a Brooklyn-Queens crosstown line were floated in the 1920s with a line going from Astoria to Bedford-Stuyvesant with a branch going west to downtown Brooklyn and another branch running south along Bedford Ave to Coney Island.
The G train is one of the shortest and least traveled lines in the system and runs through mostly residential areas like Fort Green, Bedford-Stuyvesant, Williamsburg, and Greenpoint. Originally the G served as the only local train along the Queens Blvd line and commuters had to switch at Queens Plaza for express trains into Manhattan. This service proved unpopular and the G was cut back over the years as other trains were rerouted along Queens Blvd.
On the southern section of the line the G train shares tracks with the F along the IND Culver line from Bergen St to Church Ave. Express tracks were built along this section for F trains but, as with service along Queens Blvd, commuters didn’t like having to switch trains so the express tracks remain unused.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The IRT 7th Ave line is one-half of the original Interborough Rapid Transit (IRT) subway which opened in 1904. Running from 145th St/Broadway to Times Sq at 42nd St/Broadway the original subway swung east under 42nd St and then south at Park Ave to City Hall. When this subway was expanded in 1918 service was rerouted south along 7th Ave to South Ferry and into Brooklyn to Borough Hall and Atlantic Ave.
The 1 train runs all local from Van Cortlandt Park-242nd St in the Bronx to South Ferry at the tip of lower Manhattan. From 1989 to 2005 there was an additional train, the 9, which ran as a “skip-stop” service after 96th St to speed up travel for commuters coming from upper Manhattan. Between 181st and 191st Sts the subway was dug through some of the hardest bedrock in the city and these sections are some of the deepest in the entire system.
2 and 3 trains run express from 96th St to Chambers St at which point they veer east into Brooklyn. After 96th St 2 and 3 trains swing northeast and run under Lenox Ave in Harlem. When this service opened in 1905 it helped Harlem explode with development. 3 trains terminate at 148th St while 2 trains travel into the Bronx where they run up to Wakefield-241st St along the elevated White Plains line.
In Brooklyn the 2 and 3 trains share a subway with IRT Lexington Ave 4 and 5 trains which runs through Borough Hall to Atlantic Ave, under Flatbush Ave to Eastern Parkway and out to Nostrand Ave where 3 trains continue east to New Lots Ave (elevated after Utica Ave). 2 trains run south to Flatbush Ave.
While 2 and 3 trains run express in Manhattan they only run local in Brooklyn.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The IRT Flushing line caries the 7 line (local and express service) from Times Sq-42nd St to Flushing Main St and runs from Midtown Manhattan through Long Island City, Sunnyside, Woodside, Elmhurst, Corona, and Flushing, Queens. Because of the high concentration of so many diverse ethnic enclaves though which the Flushing line runs it is colloquially known as the “International Line”.
The line has its origins well before the New York City subway opened (in 1904). Originally conceived as a commuter rail tunnel to bring Long Island trains into midtown from Long Island City the tunnel broke ground in 1892 but was shut a year later after a series of accidents. August Belmont stepped in a decade later and financed the tunnel himself as a way to run trolley cars as shuttle service. Opened in 1907, the city purchased the tunnel in 1913 to retrofit it for the expanding subway system.
The Flushing line runs elevated from Hunts Point Ave to Mets-Willets Point Ave where it dives into a short tunnel before terminating at Main St. The elevated sections of track are built with a third track for express service which only makes stops at Queensboro Plaza, Woodside-61st St, Junction Blvd, Mets-Willets Point, and Flushing-Main St. The elevated section through Sunnyside is famous for its ornately designed concrete viaduct along Queens Blvd.
In 2015 an extension west was opened to a new terminal at 34th St-Hudson Yards to serve the new mini-city growing above the LIRR train yards behind Penn Station.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-
 $30.00 – $80.00
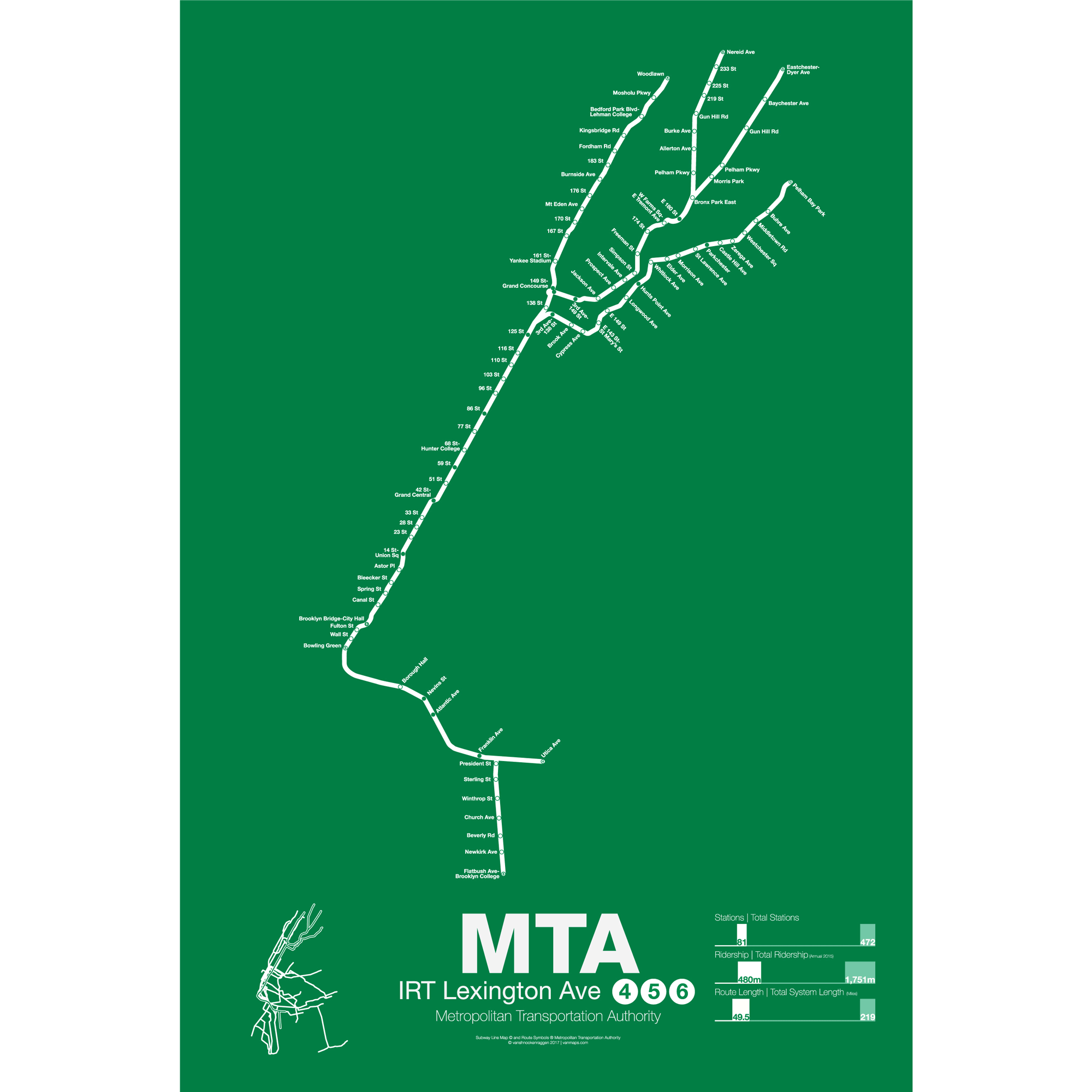
$30.00 – $80.00The IRT Lexington Ave line is one half of the original Interborough Rapid Transit (IRT) subway which opened in 1904 running from City Hall to Grand Central along Lafayette St and Park Ave South where it swung west under 42nd St to Times Sq. When the subway was expanded in 1918 service was rerouted north along Lexington Ave and into Brooklyn to Borough Hall and Atlantic Ave.
The IRT Lexington Ave line is the only subway to serve the East Side of Manhattan and averages 1.3 million riders a day, “more than the combined ridership of San Francisco and Boston’s entire transit systems”. Because of this overcrowding is a major issue and has led to the construction of a new subway under 2nd Ave. In Manhattan and Brooklyn Lexington Ave trains run exclusively underground but in the Bronx each line fans out and runs mostly elevated. The 6 train runs along the Pelham Line, a mix of elevated and subway track, and runs local and express service out through Hunts Point, Unionport, Parkchester, and terminating at Pelham Park. The 6 runs all local in Manhattan terminating at Brooklyn Bridge-City Hall.
4 trains run up to Yankee Stadium and north, elevated, along Jerome Ave to Woodlawn. 4 trains run local in the Bronx all times express in Manhattan and all times express in Brooklyn out to Utica Ave/Eastern Parkway. 5 trains join the IRT White Plains line at 149th St-Grand Concourse and shares the elevated line out to 180th St. Here service alternates between using the IRT Dyer Ave line to Eastchester and continuing with the IRT White Plains line to Nereid Ave during rush periods. 5 trains operate local in the Bronx except for rush periods when they run express from 180th St to 3rd Ave-149th St, all express in Manhattan to Bowling Green, and rush periods express to Flatbush Ave in Brooklyn.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Babylon Branch is a section of the greater Montauk Branch which runs from Long Island City to Montauk. Babylon service is electrified and runs along the Main Line from Penn Station to Jamaica and then along the Montauk Branch to Babylon. The Babylon Branch was opened in the 1860s by the South Side RR of Long Island and was leased to the LIRR in 1876. Unlike the Main Line of the LIRR, which was built for high speed travel through sparsely developed areas, the Montauk was built to serve the many small villages (now major suburban towns) of the South Shore of Long Island.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-
 $30.00 – $80.00
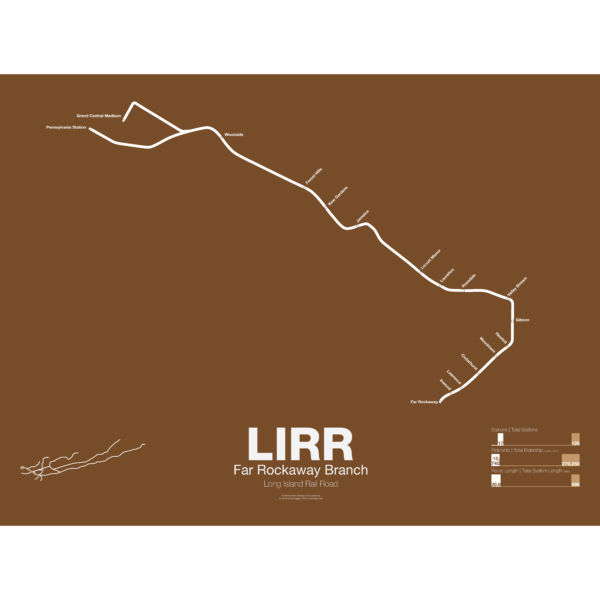
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Far Rockaway Branch was opened in 1869 by the South Side RR and initially ran all the way to Rockaway Park via southeast Queens and the Five Towns of Long Island. The branch was leased to the LIRR in 1876. In 1880 a trestle was constructed over Jamaica Bay which shortened the trip to the Rockaways. This line was run by the LIRR after 1887 and various services were run over both the Rockaway and Far Rockaway branches. In 1950 the trestle burned and instead of rebuilding it the LIRR chose to sell off the line to the City of New York which then rebuilt it as part of the A train. LIRR service was then cut back to Far Rockaway. Service runs from both Penn Station and Atlantic Terminal in Brooklyn but when East Side Access opens (scheduled 2022) all service will be routed to Penn Station.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Hempstead Branch is a short branch off the Main Line from Jamaica to Hempstead. The branch is all that remains of a much larger system, the Central Railroad of Long Island, which opened in 1873 from Flushing to Babylon. The Central RR was founded by Alexander Turney Stewart as a way to develop land in central Long Island which eventually became Garden City. Over the next 20 years the LIRR bought the rights to the Central RR and various other lines and began to consolidate them. Due to redundancy the Central RR was cut up into smaller branches and spurs and connected to the Main Line. The LIRR had a similar Hempstead Branch which ran off the Main Line at Mineola and service to Hempstead ran along both branches until 1935 when the line was consolidated due to grade separation construction.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-
 $30.00 – $80.00
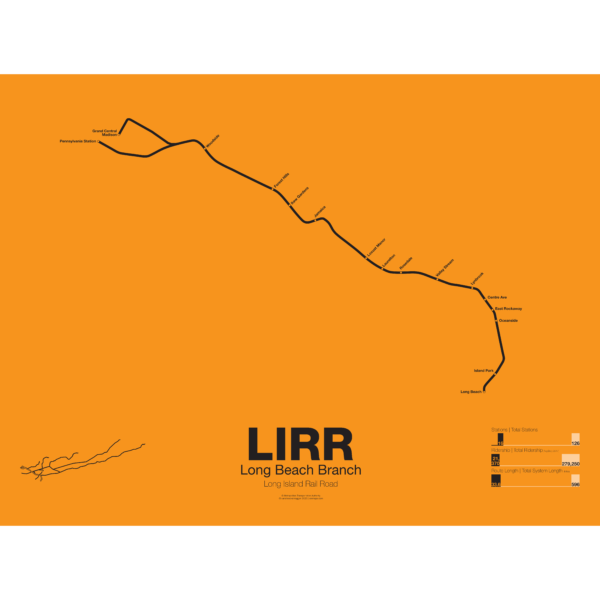
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Long Beach Branch runs from Penn Station and Atlantic Terminal To Valley Stream and down to Long Beach. It was opened by the New York and Long Beach RR Company in 1880 and the original terminal was closer to the ocean as at the time Long Beach Island had not been developed. A short extension was built to Point Lookout but service ended in 1895. Originally the line was built only to Lynbrook but was connected to the LIRR at Valley Stream in 1910.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Montauk Branch which runs from Long Island City to Montauk. The Montauk Branch was opened in the 1860s by the South Side RR of Long Island and was leased to the LIRR in 1876. While service on the Montauk uses the Main Line to Hicksville, the original South Side Main Line was what is now known as the Lower Montauk which runs a more winding route through Maspeth, Ridgewood, and Middle Village. Passenger service on the Lower Montauk ended in 1998 due to low ridership and today the tracks are used exclusively for fright. Montauk service is run express to Babylon using diesel-electric trains.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-
 $30.00 – $80.00
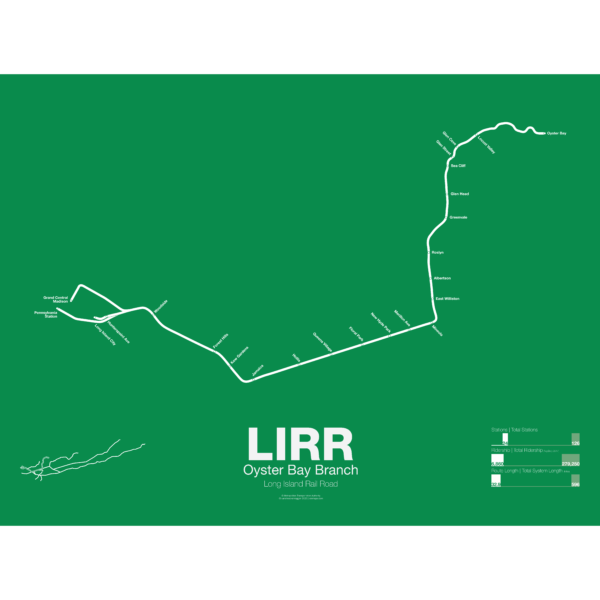
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Oyster Bay Branch opened in 1865 by the LIRR owned Glen Cove Branch RR as a branch off the Main Line at Mineola to Glen Head. The line was extended further and by 1867 it reached Locust Valley. An extension to Oyster Bay was only proposed as a counter to a rival railroad which had proposed a line to Northport. The LIRR eventually opened an extension to Oyster Bay in 1889. A large new pier was built next to the terminal for ferry service to New England. Although the line was intended to be electrified in the 1930s the work was never done and as such the line uses diesel trains which don’t run to Penn Station.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Port Jefferson Branch is a branch off the Main Line at Hicksville and was opened to Syosset in 1854. The line was extended to Northport in 1868 but due to disputes between the LIRR and the towns of Cold Spring and Huntington the new line bypassed both. In 1873 the line was extended to Port Jefferson but branched off south of Northport, leaving the original terminal a spur line that would be abandoned by 1899. In 1895 the line was extended a final time to Wading River with plans on continuing it to Riverhead, though this was never done. The Wading River extension was eventually abandoned in 1938. Due to rising ridership the LIRR is constructing a third track along the Main Line from Floral Park to Hicksville so many Port Jefferson and Ronkonkoma trains can run express to Jamaica.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Port Washington Branch runs from Penn Station to Port Washington through Flushing and is the only LIRR branch that does not run through Jamaica. Built and opened by the Flushing RR in 1854 it was the first non-LIRR railroad on Long Island. Originally the line was supposed to reach Roslyn, Oyster Bay and Huntington but this was thwarted by the LIRR which reached there first. By 1874 the Flushing RR had combined with other competitors to form the Flushing, North Shore and Central Railroad but in two years would be bought by the LIRR. Additionally there was a branch to Whitestone but this was eliminated in 1932.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Ronkonkoma Branch is the service which runs along most of the original Main Line of the LIRR from Brooklyn to Greenport through Hicksville. Service today runs to Ronkonkoma with shuttle service continuing to Greenport. The original Main Line opened from Brooklyn to Jamaica in 1836 and was extended to Hempstead in 1839. By 1844 the line had been extended out to Greenport with ferry service to New England. At the time train technology was thought too primitive to navigate the rough terrain of the Connecticut coast so a train-ferry-train service was devised to travel between New York and Boston. The LIRR Main Line ran as straight as possible down the center of Long Island, avoiding existing towns, to have the fastest service. But in 1848 a railroad was opened through Connecticut and the LIRR was now a railroad to nowhere. Over the next 30 years the LIRR grew by buying up the competition and by 1880 had a monopoly on Long Island. Today the LIRR is the oldest railroad in the country which still operates from its original charter.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR West Hempstead Branch is a short, single track line which runs from Valley Stream to West Hempstead. Most service is run as a shuttle but a few trains are through run at peak times. The West Hempstead Branch was opened by the New York Bay Extension RR Company as part of a larger, unrealized line from Brooklyn to Garden City. The line originally had complex connections to the Hempstead Branch, Main Line, and Oyster Bay Branch so that many different services could be run. Eventually these connections were eliminated due to the need for grade separation.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-
 $30.00 – $80.00
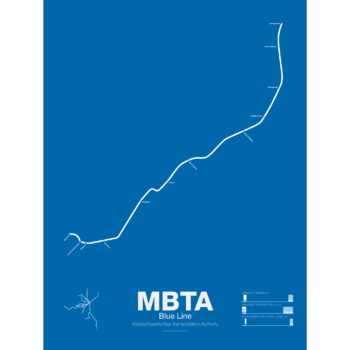
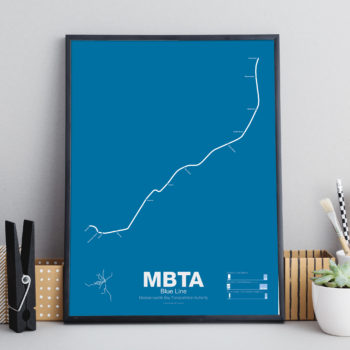
$30.00 – $80.00The Blue Line started off as a trolley tunnel to connect Scollay Sq. in downtown Boston to Maverick Sq. in East Boston. It holds the distinction as the first underwater transit tunnel (under a major body of water) opening in 1904. Initial plans called for it to be connected to the Green Line to form a subway trolley network connection all points north, east, south, and west. However, in 1924, the line was converted to heavy rail and extended to Bowdoin Sq. The Blue Line diverted traffic away from East Boston ferries which, ironically, helped bring the demise to the Atlantic Ave elevated line.
Until the 1950s the Blue Line was connected to the Red Line at Charles St so that Blue Line trains could be serviced at the Red Line train shops in Harvard Sq. In 1952 the Blue Line was extended to Suffolk Downs along the abandoned Boston, Revere Beach and Lynn Railroad and two years later extended to Revere where it still terminates at Wonderland.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The Fairmount Line is the shortest MBTA commuter rail line and the only one which runs entirely within the city limits of Boston. Originally built as part of the Norfolk County Railroad, the line opened in 1855 and was extended to Walpole, Franklin and Providence. Originally the line ran through South Boston and across the Fort Point Channel to reach its terminal. By 1898 the line had been leased to J.P. Morgan’s NY, New Haven and Hartford Railroad and when South Station opened the following year the original alignment through South Boston was abandoned. Passenger service was ended in 1944 but when the MBTA was building their Southwest Corridor rail project (rebuilding the Orange Line and Amtrak’s Northeast Corridor) they upgraded the Fairmount Line and rerouted all passenger service starting in 1979. When the Southwest Corridor opening in 1987 all service south of Readville was rerouted and the Fairmount Line was reduced to a shuttle. In the early 2000s planners and community advocates proposed adding stations and more service to the line to act as a new subway line, the Indigo Line. Four new stations were added as well as additional service but service remains less than rapid transit levels (mostly due to the use of diesel engines) and fares are higher than that of the subway and bus, limiting potential ridership.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The Fitchburg Line opened between 1840 and 1845 connecting Boston and Fitchburg. The line was extended along the northern frontier of the state before briefly running through southern Vermont on its way to Troy, NY. Traffic on the line slowed after World War 2 and by the 1960s service had been cut back as far as West Concord. After substantial investment by the state, service to Gardner was opening in 1980 but cut back again, this time to Fitchburg in 1987. In 2016 service was extended to Wachusett. The Fitchburg is the second longest line in the commuter rail system but due to decades of deferred maintenance the line suffers from the worst on time performance. Many stations are not ADA compliant and the line features many tight curves through the mountains. Until 2017 the line also had about 9 miles of single track segments which limited capacity, although today only a short section through Waltham remains single tracked.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-
 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The Franklin Line was original built as part of the Norfolk County Railroad, the line opened in 1855. Originally the line ran through South Boston and across the Fort Point Channel to reach its terminal. By 1898 the line had been leased to J.P. Morgan’s NY, New Haven and Hartford Railroad and when South Station opened the following year the original alignment through South Boston was abandoned. Passenger service ran from New York City via Waterbury and Hartford, CT but by 1966 service had been cut back to Blackstone, MA. The MBTA required towns not within their district to subsidize service themselves and only Franklin was willing to do so. Service was extended to Forge Park/495 in 1988 which was part of a separate railroad. Today service runs to Boston via the Northeast Corridor, although some rush hour trains use the Fairmount Line. Service to Foxboro is run only for football games and special events, although a new pilot program featuring weekday service to Foxboro is now being tested.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
